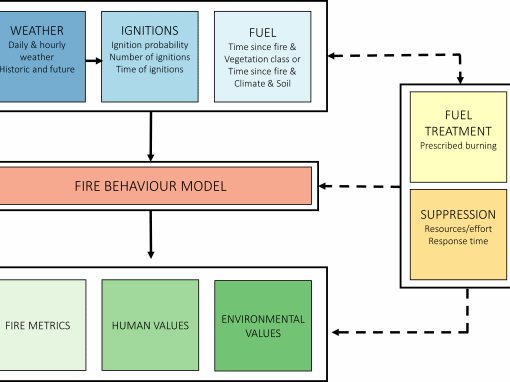
Historically, predictions of fire spread were performed manually by trained staff. Rates of spread were computed for broad areas and maps had to be plotted by hand. This required the synthesis of large amounts of information, incorporation of local knowledge and was very time-consuming. This created problems when fire managers are looking for information during emergency situations. PHOENIX was developed from 2003 to rapidly replicate the manual prediction process; accounting for changes in the weather, patterns in fuel, the efforts of firefighters and the effect of varying topography
The simulation implements a fire characterisation model capturing detail such as flame height, intensity, size, ember density, spotting and convection throughout the simulation process. Such fire predictions can help identify the potential threat to homes and buildings and indicate the likely arrival times of fire. Rapid predictions can help provide more timely warnings to communities, aid evacuation planning and help guide firefighting efforts.
PHOENIX is widely used by management agencies in southern and eastern Australia for operational fire predictions (during an event) and for fire risk modelling (prior to the fire season). Outputs from PHOENIX are used to support investment decisions, positioning of fire resources during a fire and evacuation decision making. PHOENIX is now managed by Fire Predictive Services.