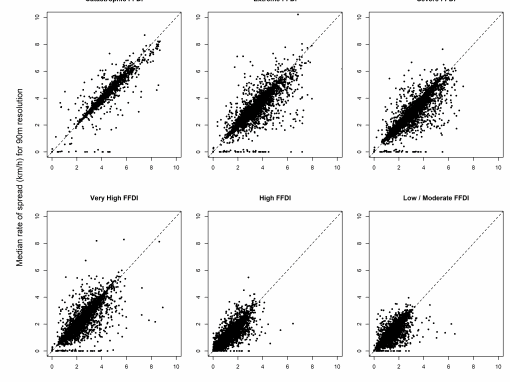
Prescribed burning is used by fire managers to alter the amount of fuel in the landscape to reduce the intensity, rate of spread and size of subsequent unplanned fires. The aim of this is to reduce the risk of wildfire impacting key human and environmental values.
The Atlas systematically investigates how risk to these values will respond to variations in the spatial location and rates of prescribed burning treatment. It provides a comprehensive and formal estimation of risk which allows users the ability to understand the likely cost, benefits and overall risk reduction for landscapes from burning activities. This means the Atlas can act as a learning and planning support tool by allowing fire managers to compare the outcomes of different prescribed burning strategies (i.e comparing strategies that incorporate combinations of landscape and edge-based burning approaches) and supports the implementation of customised prescribed burning strategies to suit the biophysical, climatic and human context of bioregions across south-eastern Australia.
This project was funded by the Bushfire & Natural Hazards Cooperative Research Centre and developed in collaboration with the University of Wollongong and Western Sydney University with the team at FLARE.